Purine Nucleotide Chemistry and Metabolism
Published: 5/25/2024
Introduction
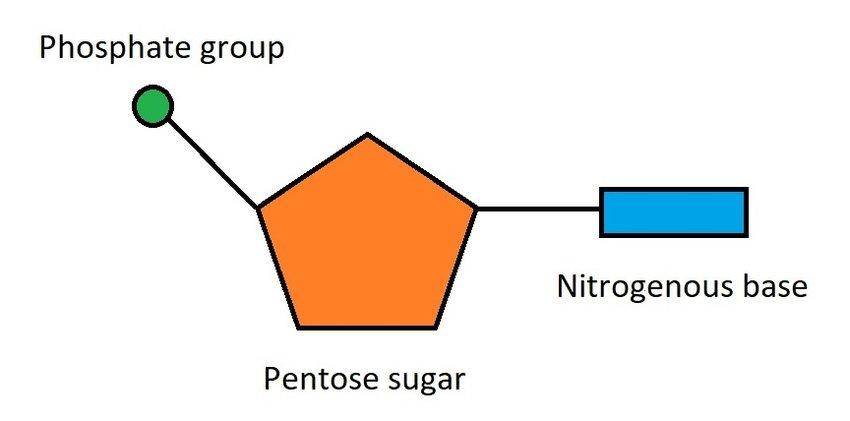
Purines are a class of nitrogenous bases, that are synthesized and metabolised in the body as a part of nucleotides, so a building block of DNA, but also has other functions. Nucleotides are the monomer that makes the DNA polymer and each nucleotide has 3 components:
- A pentose sugar (Deoxyribose or Ribose)
- A phosphate group
- A nitrogenous base
Purines are nitrogenous bases that make up DNA such as Adenine and Guanine.
Nucleosides
Yes, this isn’t a typo… Nucleosides are different from Nucleotides, but also incredibly similar. Nucleosides are nucleotides without the phosphate group, so effectively they’re just a base and a sugar.
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are nucleosides with one, two or more phosphate groups added. We actually have a neat way of naming different nucleotides based on their nitrogenous base. Take the base Adenine for example, if you add a ribose sugar to it, it’s called Adenosine. If you add a phosphate to adenosine it’s called adenosine monophosphate. If you replace the ribose sugar with deoxyribose, it becomes Deoxyadenosine, isn’t that dope?!
Check this out, you can add even more than one phosphate group.
- Adenosine + 2 phosphate groups = adenosine diphosphate
- Adenosine + 3 phosphate groups = adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Woah hold on… that’s ATP! the energy molecule! Yes, it turns out that it’s actually a triphosphate ester made from adenosine.
Functions of Nucleotides and Nucleosides
As we mentioned earlier nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA, and Nucleosides can make ATP, but they also have several other functions in metabolism such as:
- Components of co-enzymes: NAD, FAD and co-enzyme A
- Biological regulators: Cyclic AMP initiates the second-messenger cascades
Biosynthesis of purine nucleotides
This is the exciting part, how and where are purine nucleotides made in the body? well, they are mainly synthesized in the liver but are synthesized by most of the tissues as well. Inside the cell, the synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm, and happens by two important pathways: De novo synthesis and Salvage pathway.
De novo pathway
“De novo” means anew. Purine nucleotides are newly synthesized from other precursor molecules. Picture a newly manufactured car straight out of the factory with 0 mileage. Now, you might have already guessed that this is biochemistry and we’ll be mentioned a lot of different confusing names, but let’s stick to the main molecules and work our way from there.
IMP
The main parent purine nucleotide that we are concerned with is Inosine Monophosphate or IMP for short. IMP is a nucleotide composed of:
- Hypoxanthine (a purine nitrogenous base)
- Ribose
- 1 Phosphate group
IMP undergoes chemical reactions to become Adenosine monophosphate or Guaninemonophosphate, which are the end products we’re looking for.
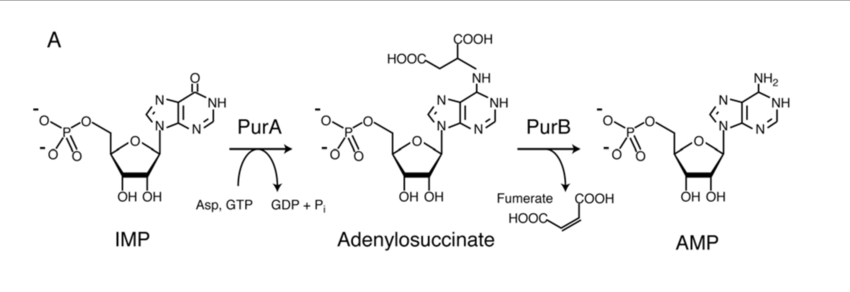
AMP from IMP
Aspertate condenses with IMP in the presence of GTP to produce adenylosuccinate which on cleavage forms AMP.
GMP from IMP
IMP undergoes NAD+ dependent dehydrogenation to form Xanthosine monophosphate. Glutamine then transfers amide nitrogen to XMP to producte GMP.
Synthesis of IMP
IMP is the direct precurso to AMP and GMP, but how do we get it in the first place? there is a chain of enzyme-regulated chemical reactions that occur to product IMP.
The major precursor to IMP is Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate or PRPP.
Ribose-5-phosphate reacts with ATP in the presence of PRPP synthetase to form PRPP. PRPP synthetase is an enzyme that is inhibited by PRPP.
Glutamine transfers it’s amide nitrogen to PRPP to replace pyrophosphate and producte 5-phosphoribosylamine in the presence of glutamyl amidotransferase. This enzyme, is inhibited by IMP, AMP and GMP, therefore it is a rate limiting step.
Salvage pathway
Free purines can be turned into purine nucleotides by the salvage pathway.
For adenine:
- PRPP donates a ribose-5-phosphate to adenine in the presence of adenine phosporibsyl transferase forms AMP
For guanine:
- PRPP donates a ribose-5-phosphate in the presence of Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase to form GMP
For Hypoxanthine:
- PRPP donates a ribose-5-phosphate in the presence of Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosy transferase to form IMP